Needs and Wants Worksheets
“Needs and Wants” worksheets are an educational tool designed to help children differentiate between essential items they need for survival and things they want for enjoyment. These worksheets are part of early education lessons, focusing on financial literacy, critical thinking, and decision-making skills. The distinction between needs and wants is crucial for building awareness of responsible consumption and the value of resources. Here is an in-depth breakdown:
1. Understanding the Concept of Needs and Wants
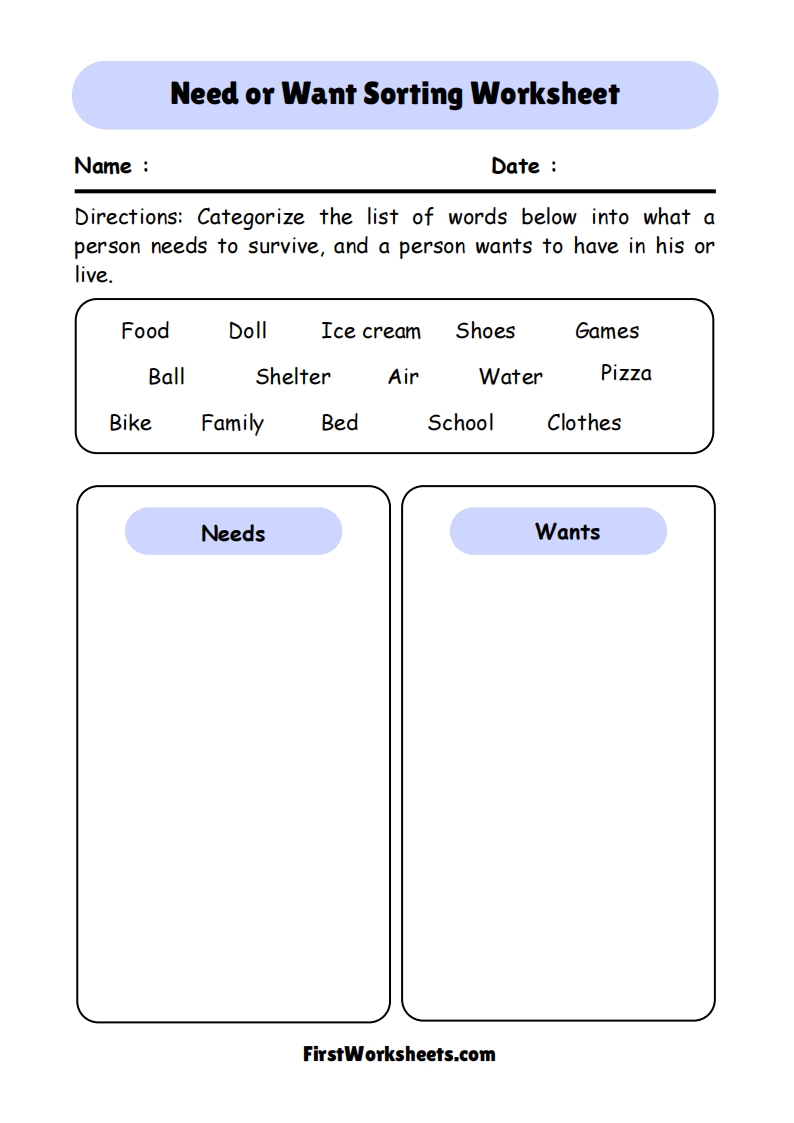
- Needs: These are essential items required for basic survival. Common examples include:
- Food
- Water
- Shelter
- Clothing
- Healthcare
- Wants: These are non-essential items that add enjoyment or convenience but are not required for survival. Common examples include:
- Toys
- Video games
- Candy
- Going to the movies
- Fancy clothing
Goal: The objective of teaching needs versus wants is to instill an understanding that while both are important, needs take priority because they are necessary for survival.
2. Components of a Needs and Wants Worksheet
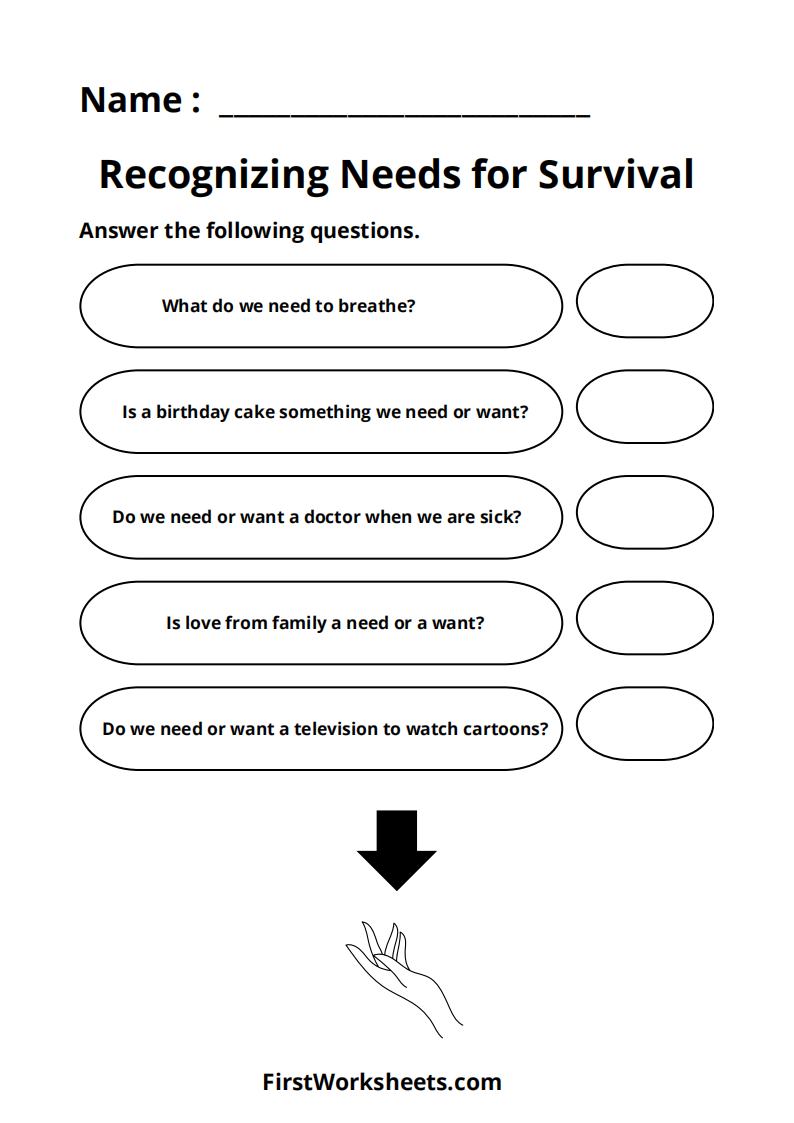
- Sorting Activity: Worksheets often include images or lists of different items, and children are tasked with sorting these into two categories: Needs and Wants. This activity promotes critical thinking and decision-making.
- Discussion Questions: Some worksheets provide questions like:
- “Why do you think food is a need?”
- “Can you live without this item?”
- “What might happen if you don’t have this need?”
- Real-Life Scenarios: Worksheets may ask children to think about situations where they have to choose between a need and a want (e.g., “If you had $10, would you buy a toy or food? Why?”).
- Prioritization Exercises: Some worksheets encourage children to rank items by importance, fostering a deeper understanding of prioritization in life.
- Word Skills and Vocabulary Development: These worksheets help children develop vocabulary related to financial literacy, consumption, and personal responsibility. They learn words like:
- Essential
- Prioritize
- Savings
- Budget
- Sacrifice
- Responsibility
3. Language Skills Developed
- Vocabulary Building: The worksheets introduce new words related to financial concepts, helping children expand their vocabulary.
- Word Sorting Skills: Children practice sorting items into categories, which improves their ability to differentiate between various types of nouns (e.g., tangible items like “clothes” vs. abstract concepts like “healthcare”).
- Comprehension and Contextual Thinking: The worksheets help children understand abstract concepts by applying them to real-world situations. For example, discussing why shelter is more important than a new toy in a particular context.
- Sentence Formation and Discussion: Some worksheets prompt children to write or verbalize sentences about needs and wants. This helps with language development, sentence structure, and explaining their thought processes.
4. Cognitive Skills Developed
- Critical Thinking: Children are required to think critically about their choices and justify why something is a need or a want.
- Decision-Making: By distinguishing between needs and wants, children develop decision-making skills that help them make informed choices in real life.
- Problem-Solving: When given hypothetical financial or resource limitations, children must decide how to allocate resources, which develops problem-solving abilities.
- Prioritization: Through ranking activities, children learn how to prioritize needs over wants, which is an essential life skill.
5. Moral and Social Development
- Understanding of Responsibility: Children learn that while wants are enjoyable, fulfilling needs comes with greater responsibility.
- Empathy and Awareness: These worksheets can also lead to discussions about poverty and the challenges some people face in meeting their basic needs, fostering empathy and social awareness.
6. Interactive and Engaging Tools
- Visual Aids: Many worksheets for younger children are highly visual, with pictures of items to help them easily identify needs and wants.
- Group Activities: Teachers might pair these worksheets with group activities where students collaborate to discuss their choices. This builds teamwork and communication skills.
- Story-based Scenarios: Some worksheets might present needs and wants in the context of a story (e.g., “Tom wants a new bike but needs school supplies”). This makes the lesson more relatable and engaging for children.
7. Practical Applications
- Budgeting: As children progress, these worksheets often segue into lessons on budgeting, teaching them how to manage limited resources effectively.
- Saving vs. Spending: These worksheets also introduce concepts related to saving money for future needs versus spending on current wants.
- Real-World Applications: Kids are encouraged to reflect on their personal experiences, which helps bridge the gap between the classroom and the real world.
8. Word Skills in Action
- Matching Words to Definitions: Children are tasked with matching words like “essential” to its correct meaning, reinforcing vocabulary.
- Identifying Synonyms: Worksheets may ask children to find synonyms for words like “want” (e.g., desire, wish) and “need” (e.g., requirement, necessity), expanding their understanding of language.
- Word Games: Some worksheets may include word searches or crosswords featuring vocabulary related to needs and wants.
“Needs and Wants” worksheets are more than just a financial literacy tool; they are a comprehensive educational resource that promotes critical thinking, decision-making, and language development. By integrating real-world examples and interactive activities, these worksheets provide children with the foundation to understand the difference between what they need and what they desire, which is an essential life skill.